We are living in the ceramics world, but we didn’t think about it deeply. Who would have thought that something most of us perceived as ‘old-fashioned’ would be something that has formed an integral part of our lives? Every day, you wake up to the buzz of the alarm clock, dash into the bathroom to have a bath, get dressed, and ultimately, drive in your car. Yet, you forget that all these items are made of Ceramics.
Ceramics have been around for quite a long time, that we often forget how useful it is and how pervasive it has come to be. The world is now a ceramic-sphere, where a ceramic item aids almost all we do. However, regardless of how essential ceramics are to us, we often know how to define them or explain what they indeed are. It’s apparent that they encompass a lot, but what exactly are ceramics?
What is ceramic?
If we begin to ponder on the concept of ceramics, we could get confused because of how broad the concept is. This is why we often try to define ceramics based on its examples or classification. If we define ceramic based on what it comprises, we would have a simple but insufficient definition because Ceramics itself is extensive.
Nonetheless, here is a straightforward definition of ceramics based on what it consists of. Ceramics can be defined as solids that encompass pottery, glasses, porcelain, tiles, bricks, diamonds, cement, and graphite.
From a chemical perspective, we can define ceramics as mineral, nonmetallic solid materials that are not acquired from organic, metallic, and carbon compounds. These inorganic and nonmetallic solids usually undergo a series of transformations which include, firing or heating, painting or glazing, and other physical or chemical transformations before the result is obtained.
Etymologically, the word ‘ceramics’ is gotten from the Greek word “Keramikos” meaning “of pottery.” This is the reason why some people regard only pottery plates as ceramic, which is incorrect.
However, it is pertinent to note that although pottery materials were only regarded as Ceramics in those days, other chemical or electrical items now have ceramics attached to them. It proves that ceramics’ notion has shifted gradually over the years, and ceramics have developed to be durable and reliable in electrical, regular, or chemical materials that pervade our everyday life.
What are Ceramics made of?
Ceramics are made of inorganic and nonmetallic solids (nonmetallic compounds). However, the basic component of ceramic is clay. The clay properties in ceramics are what give rise to terracotta, earthenware, porcelain, and stoneware. However, recently, most advanced ceramics are made of carbon, sulfur, metallic elements, and nitrogen.
In relation to the properties and overall structure of ceramics, this chemical composition gives ceramic its typical crystalline or glassy look and feel. The recent advancement of ceramics has, however, proven to negate some of its earliest believed composition.
For example, ceramics, which were thought to comprise only inorganic materials or solids, have moved towards an organic path (bone china is an excellent example of a ceramic with organic material or component).
Traditional ceramics usually comprise clay materials, feldspar, quartz, kaolinite, whereas the significant constituents of modern (advanced) ceramics are Silicon dioxide (SiO2), Aluminium Oxide (AI2O3), among others.
Ceramic History
The emergence of ceramics can initially be traced to 28000 BCE, when about a hundred figurines were found in Czechoslovakia near a kiln shaped like a horseshoe. Archeologists have also stated that a statuette called Venus of Dolní Vêstonice was found in this same area.
This statuette of a nude woman, Venus of Dolní Vêstonice, is regarded as the first ceramic artifact in the world. Also, in this period, the ceramic figurines had some ceremonial importance or significance.
Subsequently, pottery became man’s next invention. The first pottery item or material was found in Eastern Asia years after Venus of Dolní Vêstonice and the other figurines were found. Several pot fragments, whose invention was estimated to be between 18,000 and 17,000 BCE, were found in China; in the Xianrendong cave. With the appearance of Chinese pottery, Japanese and Russians grew interested in pottery, and it spread to the Eastern part of Asia in 14,000 BCE.
9,000 BCE to 1,500 BCE
The Neolithic epoch experienced a significant increase in the utilization of ceramics because of the sudden shift towards agriculture. In 9,000 BCE, the most common ceramics items made were water pots, bricks, and containers for food. During this era, the use of ceramics spread to Europe and the Middle East.
Also, during this period, the sun and the dug-out kiln were used in drying or firing the ceramics items. The temperature for firing the ceramic products in the kilns was below 1000°C and the main decorative pattern was geometric or linear.
The epoch between 7,000 BCE and 5,000 BCE marked the emergence of glass. In 7,000 BCE, people began to make sharp tools with volcanic glasses. Also, in 5,000 BCE, a man called Pliny asserted that the first glass was made by merchants from Phoenicia. However, archaeologists have not found anything that proves Pliny’s assertion.
The only proof of glass making in the world was traced to 3,500 BCE, where simple glass items like beads were produced in Egypt and Mesopotamia. However, the establishment of glassware factories started around 1,500 BCE in Egypt. Also, another significant invention that happened at about the same time as the discovery of glass items in Egypt, was the invention of the pottery wheel in 3,500 BCE.
The Common Era
Fast forward to the 16th century CE, the use of ceramics has completely spread out to several parts of the world. The industrial revolution during this time led to the invention of refractories. The refractories developed paved a way for the advancement of the ceramic industry. This advancement, however, gave rise to the emergence of more admirable properties of ceramics. For example, it was during this period that Ceramics became known to have a high melting point and low thermal conductivity.
In 1850, the first porcelain electrical insulator was developed as a result of the creation of the ceramic telegraph insulator. This groundbreaking innovation marked the beginning of the technical ceramics (engineering ceramics) era. After this period, the production and application of ceramics in different aspects of technology became more glaring.
In the 1960s, yttria-based ceramic was first invented. Some other things were also discovered or invented and spread out within and after this period. These innovations include ceramic high-temperature superconductors, bioglass, nanotechnology, polycrystalline neodymium-yttrium aluminum garnets, hyper-elastic bone, and alumina insulators.
Even with all these developments, the ceramic industry keeps developing, but its origin or history is dated back to the time when figurines and the Venus of Dolní Vêstonice were found in Czechoslovakia.
Types of Ceramics
There are several types of ceramics and they are all used to make man’s life better. The following are popular types of ceramics.
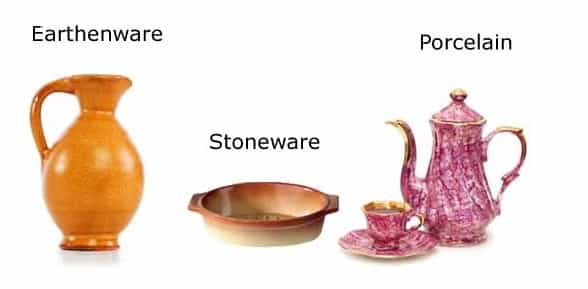
● Earthenware
This is the first ceramic that was produced by man. It dates back to 29,000 BC and was created with a fire pit. Earthenware is made with clay but is not heated as much as porcelain. Thus, it does not have the usual translucent look that porcelain and other glassy ceramics have. Since earthenwares aren’t heated to the point of vitrification, they are opaque and porous.
Properties of Earthenware
- They are usually not expensive.
- They require less time to produce.
- They are usually in brown, red, and orange colors.
- To be watertight, they must be glazed.
● Porcelain
Porcelain is an old type of ceramics that first started in China in the era of the Shang dynasty. This type of ceramic is white and made from kaolin (a clay mineral), which is heated at a very high temperature (1,200-1,400°C) in an oven (kiln). Porcelain is usually translucent and was reputable back then as an expensive item, which only the wealthy could possess. However, porcelain is still used in making exceptional decorative tableware and other expensive items.
Properties of Porcelain
- Porcelain meshes up beautifully with glazes.
- It is strong and durable.
- It is usually resistant to heat and chemicals.
● Stoneware
The stoneware is a ceramic that is heated at a temperature that exceeds the earthenware but is below the porcelain. It is made from stoneware clay and is both nonporous and watertight. This type of ceramic is popularly known to be vitreous or semi-vitreous, and although it shares similar properties with porcelain, it is not as white and as glassy as the former is.
Properties of Stoneware
- Stoneware is less porous than earthenware.
- It is more opaque than porcelain.
- It is resistant to chemicals.
● Bone China
Bone china is a type of porcelain that originated from East London. It was first produced by Thomas Fyre in 1748. This ceramic has bone ash as its main constituent and is often considered the safest tableware. The bone china was produced exclusively in the UK for about 150 years until the mid-twentieth century when Japan decided to venture into the market. However, one of its major distinctions from other ceramics is that it is a negation to the definition of ceramic as “inorganic.”
Properties of Bone China
- It is whiter, more durable, and more translucent than porcelain.
- It is made from bone ash, quartz, kaolin, and feldspar.
- It is chip-resistant.
- The amount of bone ash included determines the quality of bone china.
- It has high mechanical and physical strength.
● Fired Bricks
Fired bricks are usually burned in an oven (kiln). They are made from heating inorganic materials, which makes them durable, brittle, and capable of withstanding high temperatures.
Properties of Fired Bricks
- They are chemical resistant.
- They vary in size.
- Their attributes vary depending on the composition and producer.
- Water absorption.
- They have compressive strength.
● Titanium Carbide
This black ceramic is heat resistant and firm; it is a refractory ceramic and is usually used in producing wear-resistant items.
Properties of Titanium Carbide
- It is resistant to wear.
- Thermal conductivity.
● Glass Ceramics
Glass-ceramics are usually produced through a rigorous procedure of controlled crystallization. The end product is usually desirable and has high mechanical strength.
Properties of Glass Ceramics
- It has high chemical durability.
- It has low thermal expansion.
Other Types of Ceramics
● Carbon.
● Silicon Carbide.
● Silicon.
● Tungsten Carbide.
● Boron Carbide.
● Barium Titanate
● Bioceramic.
Uses of Ceramics
Ceramics have been useful to man right from the outset. Its usefulness can easily be summarized with how the figurines found in Czechoslovakia, even when they were both new and strange at the same time, were instrumental in certain ceremonial functions. Initially, the glassware factory in Egypt was made to produce glasses for the storage of oils and ointments.
Man has always sought a way to make things better and easier, and obviously, ceramics have helped in doing just that. However, with modernity and civilization, came a more diverse use or function of ceramic items. So, here are some uses of ceramics in the modern world that have helped make things better.
● Ceramics are used in making bricks.
● Ceramics are used in making wristwatches.
● Ceramics are used in making kitchenware.
● Ceramics are used in making cement.
● They have been used over the years to produce camera lenses.
● Ceramics have been used in making dental items e.g the artificial teeth.
● Ceramics are used in making tiles.
● Ceramics are used to produce flower vases and pots.
● Ceramics are used in making electronic devices.
● They are used in producing toilets and sanitary.
Ceramic Products
The widespread use of ceramics in the world has triggered the invention of more ceramic products. There are so many products we use that we don’t or may not even know are made of ceramics. Now, let’s take a quick dive into some of these ceramic products.
● Tiles
Tiles have become an inevitable interior and exterior decorative item for everyone. These beautiful flat-surfaced-looking items are made from ceramics, which typically means that their main constituent is clay. They are glazed to give them that enchanting look and they are often unglazed when they are produced for roofing purposes. The forms and structure of tiles are detected by their purpose. This is why tiles are grouped into two types; the common and encaustic tiles.
Common tiles are the most popular types of tiles we see around. They are simple and used for flooring, roofing, and paving. Conversely, the encaustic tiles are the ones that are mainly produced for decorative purposes. These tiles can be found on the walls of a building. The encaustic tiles are also made from regular clay and more attention is paid to detail; the color, size, design, and overall structure of the tile.
● Stoneware
All ceramic products that are produced by combining refractory clay, pottery, and stone fall into this category of products. Examples of this product include the Dome-shaped Yixing ware teapot, Wedgwood Jasperware vase, etc. In the making of stoneware ceramic products, the mixture of stone, pottery, and refractory clay is burnt at an extremely high temperature before it is glazed. Stonewares are resistant to atmospheric conditions, water, and chemicals like acid. Most stoneware ceramic products include jars, sewer pipes, toilets, basins, etc.
● Terracotta
Remember the little disk or bear you add to your hardened brown sugar to soften it? That’s terracotta! This absorbent pottery, terracotta, is made of clay and glazed with a ceramic glaze that contains lead glance (galena). They are typically soft and can even be scratched by a knife.
Terracotta as a ceramic product is used in making statues, utensils, other kitchenware, tiles, storage items (e.g., terracotta disk), bricks, and flower pots. They are useful because they possess some unique benefits or advantages: durability, ability to be easily cleaned, mouldability, resistance to atmospheric conditions and acid, inexpensive nature, and availability in a variety of colors.
● Porcelain
As you have already read in the ceramics section, porcelain is a translucent white and thin ceramic. Over the years, porcelain products have become indispensable. Porcelain is used to make tiles, sinks, plates, statuettes, figurines, porcelain jackets, and dolls.
● Clay
The principal constituent of every ceramic is clay. It is found in every ceramic product. It is used in the production of several things, including tiles, tiles, bricks, toilets, terracotta, and other types of ceramics (porcelain, stoneware, earthenware, etc.).
Examples of Ceramics

Ceramics can be found in every area of our lives. It is not difficult to find a ceramic material because it is an essential part of man’s life and has helped simplify so many tasks and the production of valuable items. Nonetheless, here are some examples of ceramics in our everyday life.
● Toilets
● Brick or Cement Houses
● Flower Vases
● Artificial teeth.
● Computer chips.
● Artificial bones.
● Bathroom tiles
● Floor tiles
● Mugs
● Plates
● Wristwatches
● Mobile phones.
● Alarm clock.
● Cars
● Spaceship
● Cookware
● Statuettes
● Picture frame.
● Light bulb.
● Decorative pottery.
● Concrete tennis court.
● Roof tiles.
● Sport items.
Properties of Ceramics
From the properties of different types of ceramics, the main properties of ceramics are deducible. However, here are some other main features of ceramics that distinguish them from other materials.
● They are refractory
Ceramics are capable of undergoing different sorts of abuses (firing and others) to get shaped into something beautiful.
● They have high melting points
This proves that ceramics are heat resistant.
● They are chemical resistant
Ceramics are usually chemical resistant because of the ionic bond found in them.
● They are hard
Ceramics are usually hard because of all the processes used in producing them. Think of the firing process, which is one reason why ceramics are known to be hard.
● They are usually scratch-proof
Ceramics are regarded as scratch-proof or scratch-resistant because they don’t show signs of scratch due to their elasticity in terms of cracking.
● They are durable
Ceramics are known to be durable owing to their molecular structure.
● They are brittle
Ceramics, regardless of how hard they may be, are prone to shattering. This is why ceramic breaks when it falls to the ground. This brittle tendency is caused by the unevenly distributed pores, which make ceramics lighter and easily broken. The basic law for this is, ‘the bigger the pores, the more prone it is to breaking.’
● Ceramics have high compressive strength.
They have high compressive strength because of the strong binding in ion and covalent bondings.
● They are wear-resistant
In ceramics, almost every good attribute is attributed to the bonding; this is also evident here as they are wear-resistant because of the bonding force.
● They have low thermal shock resistance.
The bindings in ceramics do not constitute free electrons. This is why they have low thermal conductivity.
Application of Ceramics

Ceramics are used in several industries in the world. The most common application of ceramics has been in the area of chemical engineering, electrical engineering, and mechanical engineering. However, apart from these, ceramics have been used in medicine, dentistry, food and chemical enterprises, aerospace, packaging science, mining, and many others. Here is a quick dive into how ceramics have been applied in some of these industries.
● Aerospace Industry
In the aerospace industry, ceramics have been applied in the making of exhaust and engines. Ceramics that are capable of withstanding high temperatures are also applied in the making of turbine components. They have also been applied in the making of brakes, radiators, compact optical components, and armors for helicopters.
● Medicine
Ceramics have been applied in medicine for the production of bone fillers and femoral heads for hip replacement. It has also aided the invention of pacemakers and respirators. In medicine, ceramics are generally applied for bone defects, bone augmentation, and for producing blood pumps.
● Food Industry
Ceramics have been instrumental in the production of knives, beverage dispensers, kneading rollers, kitchenware (dishes and utensils), and some conveyor tools. They are applied in the food processing industry because they are food-safe.
● Electrical and Electronics Engineering
Advanced ceramics helped this particular industry in so many ways. Most of the things we have today were produced as a result of the fascinating application of ceramics in the area of electrical and electronic engineering. Some great innovations include spark plugs, smartphones, capacitors, piezoelectric devices, inductors, magnets, resistors, and so many others.
● Textile Industry
The application of ceramic items in the textile industry has led to the production of quality thread and fabrics. In the textile industry, oxide ceramic is the true focus.
● Power Engineering
The application of ceramics in the power engineering industry is owing to the wear-resistant nature of ceramics. In this industry, monolithic ceramic materials are used to ensure that there is a standard power generation, power transport, and power storage.
● Paper Technology
Ceramic materials are used in papermaking and processing because they are resistant to abrasion.
● Optics
Owing to ceramics’ translucent look, it has been applied in the photography industry for the production of camera lenses and other lenses.
● Lifestyle and Leisure
The Venus of Dolní Vêstonice after it was discovered became relevant for ceremonial functions. Also, the invention of ceramics jewelry, wristwatches, cosmetics, and board games shows how ceramics have helped in the area of lifestyle and leisure.
● Military Engineering
Ceramics have helped in the making of military ammunition and uniforms.
Classification of ceramics
Ceramics can only be classified on the grounds of their overall makeup or composition. They can however be grouped into four categories. So, here is a classification of ceramics based on their structure.
● Non-oxide ceramics
This class of ceramics is used in making cutting tools, valves, pharmaceuticals, seals, and abrasives because of its ability to withstand wear and corrosion as well as other thermal shock problems. Non-oxide ceramics (SSiC, SiSiC, Si3N4) consist of nitrides, silicides, carbides, borides, as well as other chemical compounds.
● Oxide ceramics
Oxide ceramics contain inorganic compounds of some metalloid and metallic elements like zirconia, aluminum, silica, alumina, magnesia, silicate, among others. This class of ceramic is loved for its numerous unique attributes. These features include; high chemical resistance, broad electrical features, and the porosity of the protective coating. Oxide ceramics are used in foundry and metal processing, radiofrequency, and chemical processing, among others.
● Glass-ceramics
Many people consider glass very distinct from ceramics because while ceramics are translucent and sometimes opaque, glass is usually amorphous. However, here comes the combination of these rather distinct solids to provide a unique solid that shares unique features of ceramics and the entire processing method of glass. Glass-ceramics, which was first invented in Corning Glass Works, are polycrystalline because they are produced through a controlled crystallization method.
However, glass ceramics are grouped into seven types which include; mica apatite glass-ceramic, Lithium Disilicate glass-ceramic, mica glass-ceramic, apatite-containing glass-ceramic, leucite glass-ceramic, leucite apatite glass-ceramic, and ZrO2-containing glass-ceramic.
The overall chemical composition of glass-ceramics is the same as glass, only that glasses are 95-98% translucent. Also, the different visual properties of the glass-ceramics and the high impact resistance make it even more appealing.
● Silicate ceramics
Silicate ceramics chiefly comprises silicon and oxygen. They were very instrumental in the making of early electrical technologies. Silicate ceramics are mainly reliant on magnesium silicate or aluminosilicate.
How do you Make Ceramics?
Making ceramics is an exciting activity for anyone. You might be thinking of making your ceramic item after reading much about the historical development of ceramics, but may not know just how to go about it. You might also be wondering if you could make ceramics at home. So, here is the interesting thing about ceramics.
One amazing thing about Ceramics is that you can make them from the comfort of your home as long as you have the required materials. But what happens when you decide to make your pottery work at home and all by yourself? Here is the right way to go about making your handmade ceramic.
Rolling and the Pottery Wheel

The first thing you have to do is take and roll out your clay while ensuring that it is evened out and all chunks are rightly dissolved. It is important to note that reducing or trimming your ceramic is easier than adding to it because it could ruin the shape of your work. Next, ensure that you get the desired height or width that you want. This is solely determined by what you intend to make.
After that, you can begin molding it into whatever you intend to make. This can be done by pinching, slabbing, or coiling. Another good way of molding your ceramics can be done through the pottery wheel. But with this method, you will need to understand how the pottery wheel works and know how to use it with the clay you are working with.
If you are using the pottery wheel, ensure that you place the clay down on the dry wheel. Make sure that the clay is planted to the wheel, and if the clay seems hard, try to add little water while kneading or shaping.
Decorating and Drying
Once your clay has been molded into your desired result or item, you may decide to decorate it. Your ceramic ware can be decorated with stamps, imprints, pottery tools, and stencils to give it that pop look. After this, you can move to the drying process.
For this, you can make use of the kiln, or if you don’t have one, you must explore other options, including oven baking or air drying. For oven baking, you have to stick to the instructions as regards pre-heating and drying. You also have to ensure that you place the ceramic on a tray before putting it into the oven, then leave the ceramic in there for the required amount of time. Once you get the ceramic out, check how hard it is. Conversely, if you are air drying, ensure to place your work in a secure place and leave it to dry (this usually takes days or a week to dry).
Painting and Glazing
After your ceramic must have dried out, you will have to paint it. There are numerous paints available depending on what type of clay you used or how your ceramicware was dried. If you air dried your ware, it is recommended to utilize acrylic paints.
Also, here are some other paints available for ceramics; chalk paints and mica powder, acrylic paint, spray paints, ceramic paint, colored markers, colorants, and crayons. Always ensure to get the one that best suits your project (the type of clay you are working with and how your ware was dried).
Finally, you can apply the glaze to your pottery to make it durable and food-safe. This gives it its glassy look, and ultimately, coats your work. It is essential to use sandpaper to get any rough clay out of it before applying the glaze.
After that, your work is ready because not all glazes require firing after application. But if you still need to fire or heat your ceramic for the glaze to stay and for the vitreousness to be evident, ensure you set the temperature according to the needs of your ware because when set at an extremely high temperature, the glaze could melt and it would ruin your work.
Conversely, when the temperature isn’t high enough, your ware may not dry properly. So, it is important to follow the instructions or requirements regarding your project.
Materials Needed to Make Ceramics
Ceramics are beautiful and very useful in different aspects of our everyday life, so it is only necessary that you develop an interest in them. If you would like to make ceramics a hobby or a new-found profession or business, you will first of all need to know what materials are required for making ceramics. So, for beginners, here are some useful materials that are instrumental to the success of your ceramic project.
● Clay
In all ceramic-related projects, clay is always the key ‘ingredient’ or material in making ceramics. Now, here comes the tricky part; as a beginner, the type of clay you decide to use for your project goes a long way in determining how the ceramic would turn out.
So, if you are a newbie in the ceramic business or art, you should opt for stoneware clay as they are smooth, easy to work with, and most importantly, don’t hurt the hands. Nonetheless, when opting for any clay for your ceramic project, always make sure you lookout for the texture, clay type, price, cone size, and color.
● Ceramic glazes
Ceramic glazes are basically what you use in painting your ceramic to give it a more beautiful and vitreous feel after it has been fired. The main importance of glazes is that they make ceramics resistant to stain and safe for food.
However, as with clay, there are certain things to look out for when buying glazes. There are several types of glazes available, but when purchasing ceramic glazes for your project, ensure to check if they are gloss, transparent, opaque, breaking, or matte. These will determine how your ceramic ware would turn out after it has been fired.
● Pottery wheel
Getting a pottery wheel isn’t compulsory, but it is necessary because it helps you molding your clay evenly. It helps you in ensuring that all sides are equal and all edges are evenly curved. But if you decide to mold and shape your clay with your hands because of how expensive getting a pottery wheel maybe, that is fine. However, if you are making ceramics as a business, you need professionality, which is guaranteed by the pottery wheel.
● Kiln
Purchasing a kiln can be quite expensive. This is highly recommended for everyone who ventures into ceramic making either as a business or hobby. The kiln is used in firing your already molded work to ensure that your work is durable. It also keeps the glaze intact to produce the vitreous look that is typical of every ceramic.
● Potter’s needle
You need a potter’s needle to carefully trim the top surfaces of your clay while molding or shaping clay on the pottery wheel.
● A Towel
You need a towel while doing your pottery work to ensure that you wipe your hands when the need arises. It also helps to prevent you from getting stained from the clay.
● A wooden trimming tool
You need some modeling tools to help you in removing excess clay from your molded work.
● A bamboo brush
Brushes are the major tools used in applying glazes. However, they are also used for decorative purposes. A large soft Sumi or bamboo brush will be fantastic for your ceramic project.
● Apron
Aprons are meant to protect you and your clothes from getting clay all over you while throwing.
● Sponge
In every ceramic or pottery project, you will have to wipe the surfaces of the clay to remove any additional splash of clay from your work.
Ceramics FAQs

● Is ceramic stronger than steel?
Ceramics are generally stronger than steel. A ceramic wristwatch, for example, is said to be four times stronger than stainless steel.
● Is ceramic breakable?
Although ceramics are hard and durable, they are prone to breaking. So, yes, ceramics are breakable, and the unevenly distributed pores cause this in them.
● Is ceramic scratch resistant?
Ceramic is scratch-resistant because it always retains its original translucent look. This leaves it always looking new and resistant to scratch unless it falls to the ground and cracks or breaks.
● Why is ceramic so expensive?
Ceramics are expensive to acquire (that is why the Ru Guanyao brush washer was sold for $37.7 million), but it all depends on what type of ceramic you want. Also, if you decided to venture into the world of ceramics as a hobbyist, you will have to get prepared to buy a kiln, clay, and other materials. The essential thing to note here is that although the raw materials used in making ceramics are easily affordable, the making process is quite expensive. This is where all the money goes in.
● Is ceramic harder than titanium?
Titanium, one of the strongest metals in the world, is harder than ceramics because ceramics are generally brittle. When a ceramic breaks as a result of its brittle nature, titanium remains hard in its initial state, which makes it harder and more durable than ceramics.